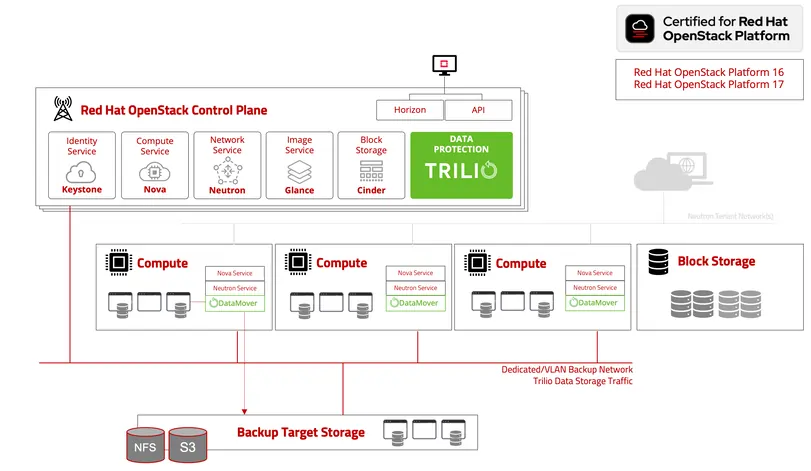
Red Hat OpenStack Backup and Recovery
Trilio for Red Hat OpenStack is one of the factors that has enabled us to become a Tier 1 partner of Red Hat and is fully integrated into Red Hat OpenStack Platform
100% Native Red Hat OpenStack Protection
Protect and Restore Virtual Machines with Trilio One-Click Restore
Watch the video to see the simplicity of restoring Virtual Machines and all of their associated Cinder Volumes, Network information and Metadata with a one-click restore.
Designed exclusively for Red Hat OpenStack
Multi-Tenant
Role-based access for secured zones within your cloud
Agentless
A Trilio data mover runs behind the scenes as part of the Nova compute node
Non-Disruptive
Full and Incremental snapshot capture of entire workloads
OpenStack Integrated
Fully integrated as a service in OpenStack, documented RESTful API and native OpenStack CLI
Self-Service
Backup & restore workloads via the OpenStack Dashboard or OpenStack Command Line
Scalable
Linear scale with zero degradation
Configurable Recovery
Select components of your build to recover
Trilio is a Tier 1 Partner of Red Hat
Trilio has been providing enterprise protection for Red Hat OpenStack Platform since RHOSP10. With RHOSP18 around the corner, trust the backup solution designed for OpenStack.
With Trilio and Red Hat, you receive Enterprise class, backup-as-a-service whether you are a small business, telco operator or managed service provider.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is included in your Backups ?
Trilio performs application-centric backups, meaning Trilio includes everything which is required to be able to recover your entire application
Trilio collects the following during a backup:
- Complete Disk Volumes (Boot and Cinder) at the Block Storage Level
- Complete Network Topology (including Subnets, Networks, Ports and capture MAC address)
- Storage Volumes from Cinder, or directly from Ceph for very efficient backups
- Cinder Volume Configuration, Cinder Types, Metadata
- Security Groups and Keys
- VMs (Single or Multiple VMs)
- VM Metadata & Flavors (Size of VMs)
- Boot Image and overlays
How can you restore Workloads ?
There are a multiple options to recover your workloads.
- Operational Recovery (on the fly)
- Disaster Recovery
- Test/Dev
- New Availability Zone
- New Clouds
- Files/Folder-Level Restore
Who is enable to restore workloads ?
In general it is up to your Role-Based-Access-Control policy who gets the permission to recover workloads and applications.
Common Roles are for instance:
- Cloud Administrators
- Backup Administrators
- Tenants / Project User
Ready to See Trilio for OpenStack in Action?
Success Story
Telefonica Shares Success Story
OpenStack Backup and Recovery Use Cases
OpenStack Backup and Recovery
Recover any OpenStack application quickly in the event of data loss or misconfiguration. Trilio enables easy restoration of entire workloads that reflect the clouds last best-known state. Such as One-Click-Restore to entire project recovery on different clusters.
Migration
A tenant or administrator can capture an application and its data and non-disruptively migrate that exact point-in-time to another OpenStack cloud. The need to migrate OpenStack workloads can be driven by economics, security or test/dev.
Disaster Recovery
Recover any OpenStack application quickly in the event of a disaster. Trilio enables easy restoration of entire workloads that reflect the clouds last best-known state. Trilio makes OpenStack disaster recovery easy.
Network Functions Virtualization backup and recovery (NFV)
Business critical services like NFV can quickly be configured to any state, assuring the optimal quality of service. Trilio provides recovery from data damage and allows restoration of entire VNFs, selected VNFs, or individual data items using a point-in-time working copy. The platform also allows recovery from a disaster by restoring the OpenStack network topology and populating it with a working copy of the entire NFV.