In today’s digital age, businesses heavily rely on their data and applications to keep things running smoothly, but sometimes, disasters can happen like natural calamities, human errors, cyber-attacks, hardware or software failures, and all sorts of other things that can cause chaos.
Disaster Recovery, how it will help you
When these disasters strike, they can disrupt your business operations, cause data loss, and lead to financial and reputational harm. That’s why having a disaster recovery plan (DRP) is really important for you. DR is basically a set of policies, tools, and procedures that help your organization prepare for and recover from disasters.
In this blog, we will provide an overview of why disaster recovery is crucial for your business and what you can do to make sure your organization is ready in case of a disaster, as more industries require disaster recovery plans and as part of compliance they need to test their recovery plans on a regular basis and attack vectors like cyberattacks or ransomware are rising.
Definition
Disaster recovery refers to the process of restoring IT infrastructure and services after a disaster. It involves recovering data, applications, and systems to a previous state, typically through backups, replication, or failover. Disaster recovery aims to minimize the impact of disasters on business operations, reduce downtime, and ensure data and applications are available when needed.
It involves creating and implementing procedures and technologies to recover from disasters and ensure business operations continue with minimal disruption. Disaster recovery plans (DRPs) outline the steps necessary to recover from disasters and the tools and resources required to execute those steps.
Also read this for more information: Trilio for Disaster Recovery
8 facts – The Increasing complexity of Disaster Recovery

Platform Architectures
- You maybe have large service meshes to protect.
- Distributed tiny workloads across regions and cloud providers – combined into one customer-facing product that needs data protection.
- More automation than ever accelerates the creation of workloads.
- IoT, Edge computing is everywhere.
- Many companies sell APIs and their functionality to others.
- Service Ecosystems (high dependencies).
- Huge complexity with the actual order of data/application restores.
- Risk of service bottlenecks.
Types of Disasters
Disasters can be broadly classified into two categories:
Natural disasters and man-made disasters.
Natural disasters include events such as floods, earthquakes, hurricanes, and wildfires.
Man-made disasters can be intentional or accidental and include cyber-attacks, power outages, hardware or software failures, and human errors.
5 Steps to plan your Disaster Recovery
The disaster recovery planning process involves several steps, including:
- Conduct a business impact analysis to determine the potential impact of disasters on business operations.
- Identify critical applications, data, and systems that need to be recovered quickly.
- Define recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) for each application, data, and system.
- Develop a disaster recovery plan that outlines the steps necessary to recover from disasters and the tools and resources required to execute those steps.
- Test the disaster recovery plan regularly to ensure it works as intended.
Disaster Recovery Plan Components.
6 Crucial Components for Your Disaster Recovery Plan
- Roles and responsibilities of the disaster recovery team.
- Contact information for the disaster recovery team, vendors, and stakeholders.
- Procedures for backup and recovery of data, applications, and systems.
- Procedures for failover and failback of systems and applications.
- Procedures for communication during and after a disaster.
- Test and maintenance procedures.
Why should you care about Disaster Recovery Planning
Organizations must have a disaster recovery plan in place to ensure business continuity in the face of unexpected events or disasters.
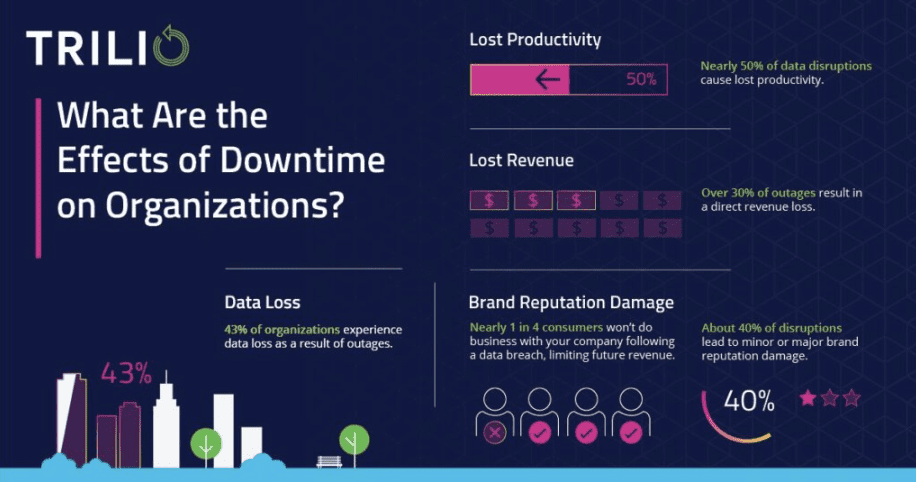
More Details and Facts and Figures? Check this out.
By creating a disaster recovery plan, organizations can prepare for the worst-case scenario and ensure that critical systems and data are protected and recoverable. Disaster recovery planning involves identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities, creating backup and recovery procedures, and testing and updating the plan regularly to ensure that it remains effective.
Without a well-designed disaster recovery plan, organizations may be unable to recover from disasters and could suffer significant financial losses, damage to their reputation, and even legal consequences. By investing in disaster recovery planning, organizations can minimize the impact of disasters and maintain continuity of operations even in the face of unexpected events.
Further Articles
RTO vs RPO
https://trilio.io/resources/rto-and-rpo/
Continuous Restore to improve RTO
https://trilio.io/products/intelligent-recovery-with-trilios-continuous-restore/

